Meet QuestDB: The High-Performance Time-Series Database
Introduction
In today's data-driven world, handling large volumes of time-series data efficiently is critical for many industries, including finance, IoT, and real-time analytics. QuestDB stands out as an open-source time-series database designed for high throughput ingestion and fast SQL queries. This blog post aims to provide a detailed technical overview of QuestDB, exploring its architecture, features, and performance advantages, as well as practical guidance on how to get started with QuestDB.
What is QuestDB?
QuestDB is an open-source time-series database engineered for high-performance data ingestion and query execution. It is well-suited for applications involving financial market data, IoT sensor data, ad-tech, and real-time dashboards. QuestDB supports high cardinality datasets and can act as a drop-in replacement for InfluxDB by supporting the InfluxDB Line Protocol.
Key Features
- High Throughput Ingestion: Capable of handling millions of records per second.
- Fast SQL Queries: Optimized for complex queries with low latency.
- ANSI SQL with Time-Series Extensions: Combines standard SQL with specialized functions for time-series data.
- Column-Oriented Storage: Enhances performance for analytical queries.
- Parallelized Vector Execution: Utilizes multi-core processors efficiently.
- SIMD Instructions: Further boosts performance by parallelizing computations at the hardware level.
- No External Dependencies: Built from scratch in Java, C++, and Rust, avoiding garbage collection pauses.
Architecture and Design
Column-Oriented Storage
QuestDB uses a column-oriented storage model, which is ideal for time-series data. This approach stores each column of data contiguously on disk, improving the efficiency of read and write operations, especially for analytical queries that typically access a subset of columns.
Parallelized Vector Execution
QuestDB leverages modern CPU architectures by parallelizing data processing across multiple cores. This parallelized vector execution allows QuestDB to perform operations on large chunks of data simultaneously, significantly reducing query execution times.
SIMD Instructions
Single Instruction, Multiple Data (SIMD) is a technique used to perform the same operation on multiple data points simultaneously. QuestDB utilizes SIMD instructions to accelerate various computational tasks, further enhancing performance.
No Garbage Collection
QuestDB's codebase is designed to avoid garbage collection, a common source of latency spikes in high-performance systems. By using a combination of Java, C++, and Rust, QuestDB achieves real-time performance without the interruptions caused by garbage collection pauses.
Querying Time-Series Data
SQL Extensions
QuestDB extends ANSI SQL with time-series specific functions, making it easier to filter, aggregate, and analyze time-series data. Some key SQL extensions include:
- Sample By: Allows downsampling of data.
- Latest On: Retrieves the latest records for a given condition.
- Time-Partitioned Joins: Enables efficient correlation of time-series data from different sources.
Example Queries
To illustrate the power of QuestDB's SQL extensions, consider the following example queries:
Sum of a Column:
SELECT sum(trip_distance) FROM trips;Sum and Average of Columns:
SELECT sum(fare_amount), avg(fare_amount) FROM trips;Average Over a Time Period:
SELECT avg(trip_distance) FROM trips WHERE pickup_datetime IN '2019';Downsampled Average by Hour:
SELECT pickup_datetime, avg(trip_distance) FROM trips WHERE pickup_datetime IN '2019-01-01' SAMPLE BY 1h;Latest Record for Each Symbol:
SELECT * FROM trades LATEST ON timestamp PARTITION BY symbol;
Installation and Setup
Docker
One of the easiest ways to get started with QuestDB is by using Docker. The following command will pull the QuestDB Docker image and start a container:
docker run -p 9000:9000 -p 9009:9009 -p 8812:8812 questdb/questdb
Homebrew (macOS)
macOS users can install QuestDB using Homebrew:
brew install questdb
brew services start questdb
To manage QuestDB, you can use the following commands:
questdb start // To start QuestDB
questdb stop // To stop QuestDB
Direct Downloads
QuestDB provides direct download options for various platforms. Visit the QuestDB downloads page for more details.
QuestDB Cloud
For those looking for a fully managed solution, QuestDB Cloud offers additional features such as role-based access control, cloud-native replication, compression, and monitoring. New users can get started with $200 credits.
Connecting to QuestDB
QuestDB provides multiple interfaces for interacting with the database:
- Web Console: An interactive SQL editor accessible on port
9000. - InfluxDB Line Protocol: For streaming ingestion, also on port
9000. - PostgreSQL Wire Protocol: For programmatic queries and transactional inserts on port
8812. - REST API: For bulk imports and exports via HTTP.
Web Console
The QuestDB Web Console is a powerful tool for running SQL queries and visualizing data. It also supports CSV import, making it easy to load data into the database.
InfluxDB Line Protocol
QuestDB supports schema-agnostic streaming ingestion using the InfluxDB Line Protocol. This allows for seamless integration with systems that already use InfluxDB for data ingestion.
PostgreSQL Wire Protocol
By supporting the PostgreSQL Wire Protocol, QuestDB enables programmatic access using PostgreSQL client libraries. This makes it easy to integrate QuestDB with existing applications that use PostgreSQL.
REST API
QuestDB's REST API provides endpoints for importing and exporting data in CSV format, as well as for executing SQL queries via HTTP.
Data Ingestion
QuestDB offers several official clients for ingesting data using the InfluxDB Line Protocol. These clients support various programming languages, including:
- .NET: QuestDB .NET Client
- C/C++: QuestDB C/C++ Client
- Go: QuestDB Go Client
- Java: QuestDB Java Client
- NodeJS: QuestDB NodeJS Client
- Python: QuestDB Python Client
- Rust: QuestDB Rust Client
Example Ingestion Using Python
Here is an example of how to ingest data into QuestDB using the Python client:
import questdb.ingress as qdb
import pandas as pd
# Create a QuestDB client
client = qdb.Client(host='localhost', port=9009)
# Create a DataFrame with sample data
data = {
'timestamp': ['2023-01-01T00:00:00Z', '2023-01-01T01:00:00Z'],
'symbol': ['AAPL', 'GOOGL'],
'price': [150.75, 99.99]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Ingest the DataFrame into QuestDB
client.ingest_dataframe(table_name='stocks', df=df)
Query Performance
QuestDB is designed to handle high-throughput ingestion and execute queries with low latency. Here are some example queries and their execution times on a QuestDB instance running on a c5.metal instance using 24 cores:
| Query | Execution time |
|---|---|
SELECT sum(trip_distance) FROM trips |
0.15 secs%20FROM%20trips;&executeQuery=true) |
SELECT sum(fare_amount), avg(fare_amount) FROM trips |
0.5 secs,%20avg(fare_amount)%20FROM%20trips;&executeQuery=true) |
SELECT avg(trip_distance) FROM trips WHERE pickup_datetime IN '2019' |
0.02 secs%20FROM%20trips%20WHERE%20pickup_datetime%20IN%20%272019%27;&executeQuery=true) |
SELECT pickup_datetime, avg(trip_distance) FROM trips WHERE pickup_datetime IN '2019-01-01' SAMPLE BY 1h |
0.01 secs%20FROM%20trips%20WHERE%20pickup_datetime%20IN%20%272019-01-01%27%20SAMPLE%20BY%201h;&executeQuery=true) |
| `SELECT * FROM trades LATEST ON timestamp |
PARTITION BY symbol` | 0.00025 secs |
Comparing QuestDB to Other Time-Series Databases
When evaluating QuestDB, it's useful to compare it to other popular time-series databases such as InfluxDB and TimescaleDB. QuestDB has been benchmarked to outperform these databases in various scenarios, particularly in terms of ingestion rate and query performance.
Ingestion Rate Comparison
In a benchmark comparing QuestDB, InfluxDB, and TimescaleDB, QuestDB demonstrated a significantly higher ingestion rate. The following chart illustrates this comparison:
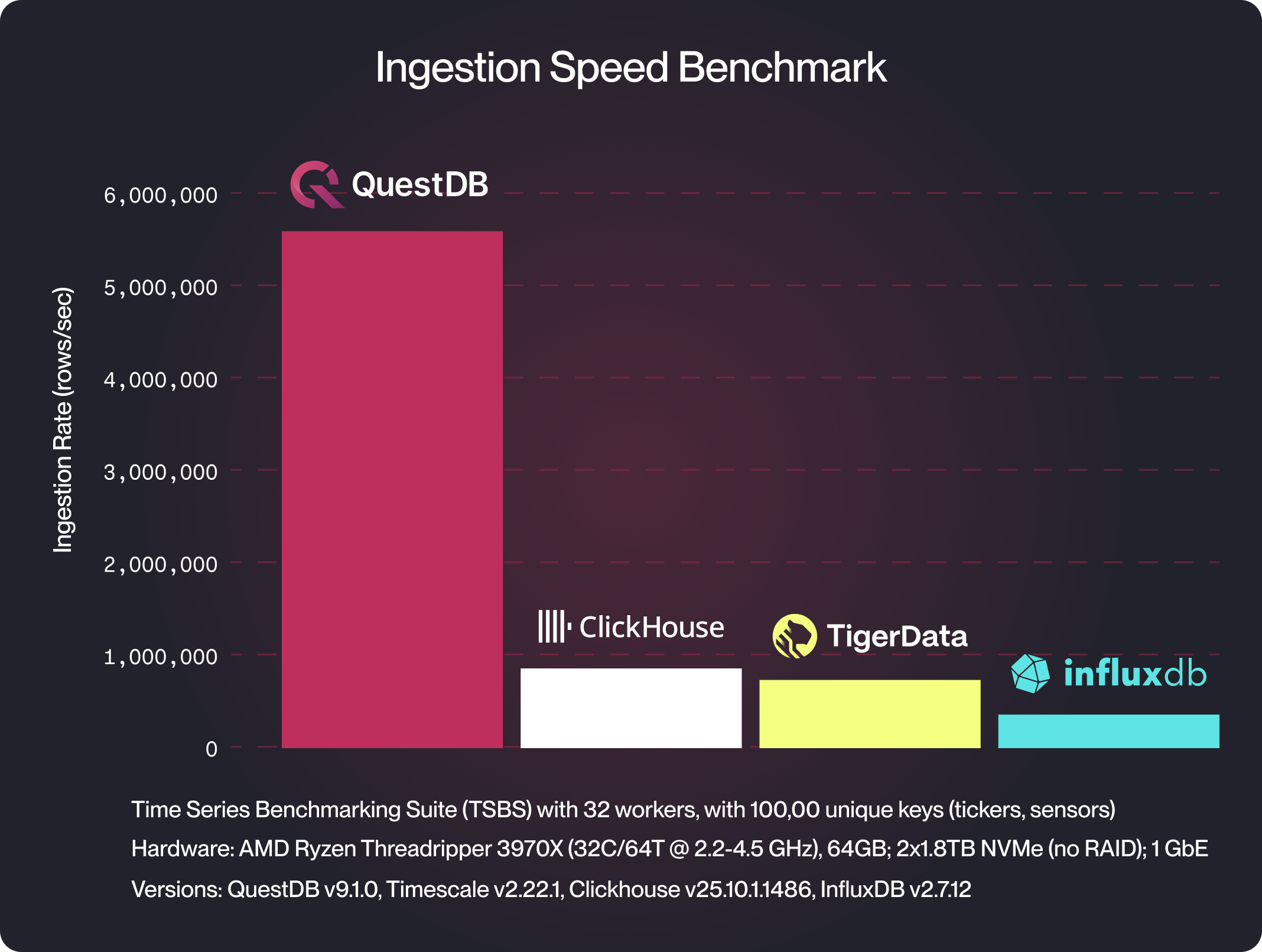
Query Performance Comparison
QuestDB also excels in query performance. For instance, typical queries on large datasets return results in a fraction of the time required by competing databases. This makes QuestDB particularly well-suited for real-time analytics and time-sensitive applications.
Use Cases
Financial Market Data
QuestDB's high ingestion rate and low-latency queries make it ideal for financial market data, where large volumes of trade and price data need to be ingested and analyzed in real-time.
IoT Sensor Data
In IoT applications, QuestDB can handle the continuous stream of data from thousands of sensors, allowing for real-time monitoring and analytics.
Ad-Tech
Ad-tech platforms can leverage QuestDB to store and analyze large volumes of ad impression and click data, providing insights that drive revenue optimization.
Real-Time Dashboards
QuestDB's integration with tools like Grafana enables the creation of real-time dashboards that provide instant visibility into key metrics and trends.
Resources and Support
Documentation
- QuestDB Documentation: Comprehensive guides on how to run and configure QuestDB.
- Tutorials: Step-by-step tutorials to explore QuestDB's capabilities.
- Product Roadmap: Insights into upcoming features and releases.
Community Support
- Community Slack: Join the community to discuss technical issues, share experiences, and ask questions.
- GitHub Issues: Report bugs or request new features.
- Stack Overflow: Find answers to common questions and troubleshooting tips.
Deployment Options
QuestDB can be deployed on various platforms, including:
Conclusion
QuestDB is a powerful time-series database designed to handle the demands of modern data-driven applications. Its combination of high throughput ingestion, fast query performance, and operational simplicity makes it an excellent choice for a wide range of use cases, from financial market data to IoT and real-time analytics. Whether you're looking to replace an existing time-series database or start a new project, QuestDB offers a robust and scalable solution.
For those interested in exploring QuestDB further, the live demo provides a hands-on experience with sample datasets, and the quickstart repository offers a comprehensive walkthrough of its capabilities. With extensive documentation, community support, and various deployment options, QuestDB is well-positioned to meet the needs of developers and businesses alike.













